Pipe corrosion, driven by material composition, environmental factors, and aggressive substances, is a major issue. Understanding common causes like material type (copper, steel, PVC), corrosive fluids/gases, moisture, humidity, poor drainage, and inadequate ventilation is key to prevention. Copper forms protective patina layers, making it resistant in non-aggressive environments; steel rusts due to iron content and factors like moisture, carbon dioxide, and bacteria; while PVC's synthetic nature makes it immune to corrosion. Choosing materials like PVC, which resists all forms of corrosion, based on these common causes ensures long-lasting piping systems.
In the world of plumbing, understanding pipe corrosion is paramount to ensuring durable, long-lasting infrastructure. This article delves into the age-old question: which pipes corrode fastest—Copper, Steel, or PVC? By exploring the common causes and factors contributing to pipe corrosion, we provide a comprehensive analysis comparing these three materials’ resistance to time’s relentless effect. Armed with this knowledge, readers can make informed decisions when selecting pipes for optimal longevity.
- Understanding Pipe Corrosion: Common Causes and Factors
- A Comparative Analysis: Copper, Steel, and PVC's Resistance to Corrosion
- Practical Implications: Choosing the Right Pipes for Longevity
Understanding Pipe Corrosion: Common Causes and Factors
Understanding Pipe Corrosion: Common Causes and Factors
Pipe corrosion is a natural process that occurs when certain materials react with moisture, oxygen, or other elements present in the environment. In terms of common causes of pipe corrosion, several factors come into play. Primarily, the type of material the pipes are made from plays a crucial role. Copper, steel, and PVC each have distinct properties that influence their resistance to corrosion. For instance, copper is highly resistant due to its natural oxidation layer, while PVC’s inertness to chemicals and moisture makes it less prone to corrosion.
Other common causes include exposure to aggressive fluids or gases, excessive moisture, high humidity, poor drainage, and inadequate ventilation. Over time, these factors can accelerate the corrosion process, leading to pipe degradation and potential failures. Understanding these causes is essential for selecting the right type of pipes for specific applications and implementing effective maintenance strategies to prevent or slow down corrosion.
A Comparative Analysis: Copper, Steel, and PVC's Resistance to Corrosion
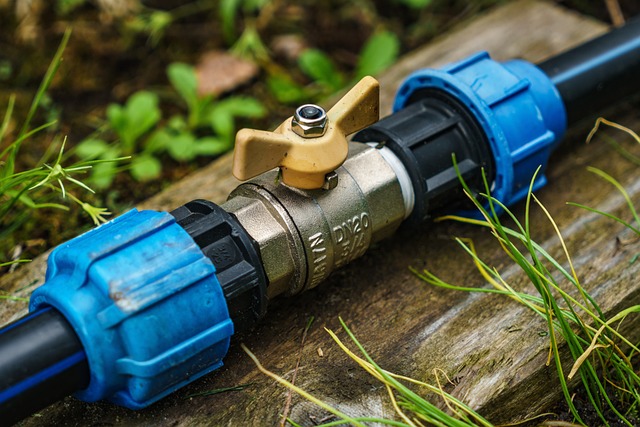

Copper, steel, and PVC are commonly used materials for pipes, each with its unique properties regarding resistance to corrosion. When considering which material corrodes fastest or slowest, understanding their inherent corrosion mechanisms is key. Copper, known for its excellent electrical conductivity, develops patina when exposed to moisture and oxygen, forming a protective layer that slows down further oxidation. This natural protection makes copper resistant to many forms of corrosion, especially in non-aggressive environments.
Steel, on the other hand, is susceptible to both uniform and localized corrosion due to its iron content. Common causes of pipe corrosion include moisture penetration, carbon dioxide ingress, and bacterial growth. In the presence of these factors, steel pipes can experience significant degradation over time, leading to rust formation and structural compromise. PVC (polyvinyl chloride) pipes offer a different perspective; being a synthetic material, it is inherently resistant to many types of corrosion. Its stability under various environmental conditions makes PVC a popular choice for applications where common causes of pipe corrosion, such as moisture and chemical exposure, are prevalent.
Practical Implications: Choosing the Right Pipes for Longevity

Choosing the right pipes for longevity involves understanding the common causes of pipe corrosion and selecting materials that best resist these issues. Copper and steel, both commonly used piping materials, exhibit differing resistance to corrosion. Copper, known for its natural resistance to oxidation and bacteria, is less prone to corrode in moist environments but can be susceptible to pitting when exposed to salts or certain chemicals. Steel pipes, stronger and more versatile, require additional protective coatings like galvanization or plastic liners due to their higher susceptibility to rusting, especially in humid conditions or when exposed to corrosive substances.
On the other hand, PVC (polyvinyl chloride) pipes offer a highly effective solution for longevity as they are virtually immune to corrosion. This makes PVC an excellent choice for both indoor and outdoor applications, particularly in environments prone to high moisture levels or exposure to chemicals commonly found in household or industrial settings. By considering the common causes of pipe corrosion, such as moisture, salt, and chemicals, homeowners and professionals can ensure the longevity of their piping systems by selecting materials like PVC that are designed to withstand these challenges.
In understanding the common causes of pipe corrosion, it’s evident that material choice plays a pivotal role in determining a pipe’s longevity. Our analysis reveals that while copper and steel have their advantages, PVC emerges as a top contender for resistance to corrosion. When considering practical implications, selecting the appropriate pipe material can significantly extend the lifespan of plumbing systems, averting costly repairs and disruptions. By choosing pipes with enhanced corrosion resistance, homeowners and contractors alike can ensure efficient, lasting performance, addressing the crucial aspect of preventing pipeline degradation over time.
